What is a The USB Flash Drive?
A USB flash drive is a portable storage device that connects to computers and other devices via a USB interface. It is used for quickly storing and transferring files (such as documents, photos, videos, etc.).
It is small in size, plug-and-play, and does not require additional drivers (modern systems usually recognize it automatically). Its capacity ranges from a few GB to several TB, making it a common tool to replace optical discs and floppy disks.
What are the names of USB flash drives, and which ones are most commonly used?
The most common name for a USB flash drive in the world. In formal occasions or technical documents, it is also called “USB Pendrive” or “USB Flash Disk“. Other common names include “USB memory” (emphasizing the storage technology), “USB flash pendrive” (evolved from an early brand name), as well as “随身碟 (suí shēn dié)” commonly used in Taiwan and “USB memory stick” in Hong Kong.
In an English environment, the most standard term is “USB flash drive“. Americans are used to saying “thumb drive“, while in places like India, “pen drive” is more commonly used.
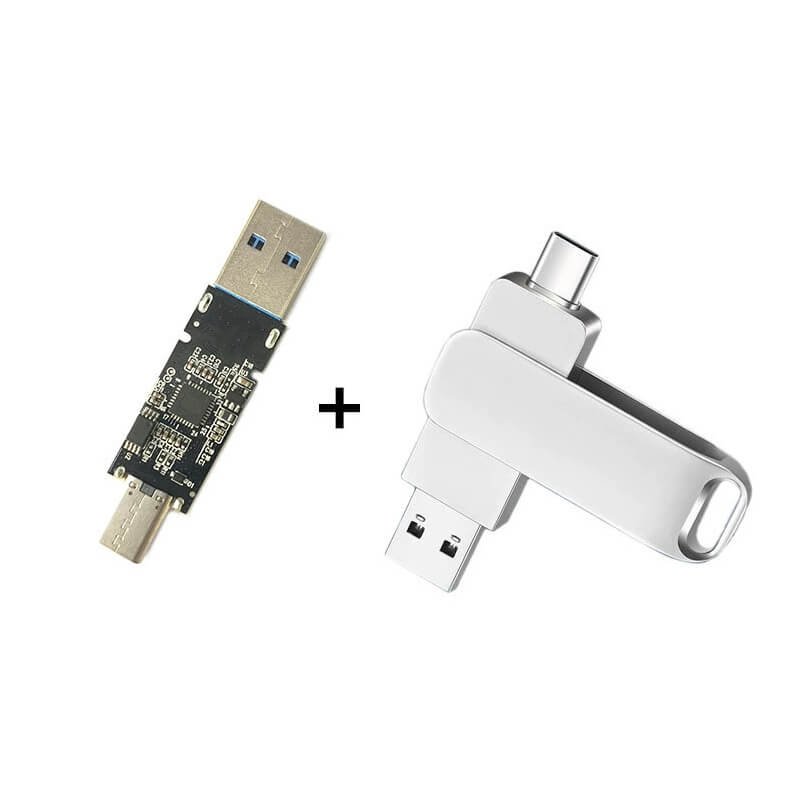
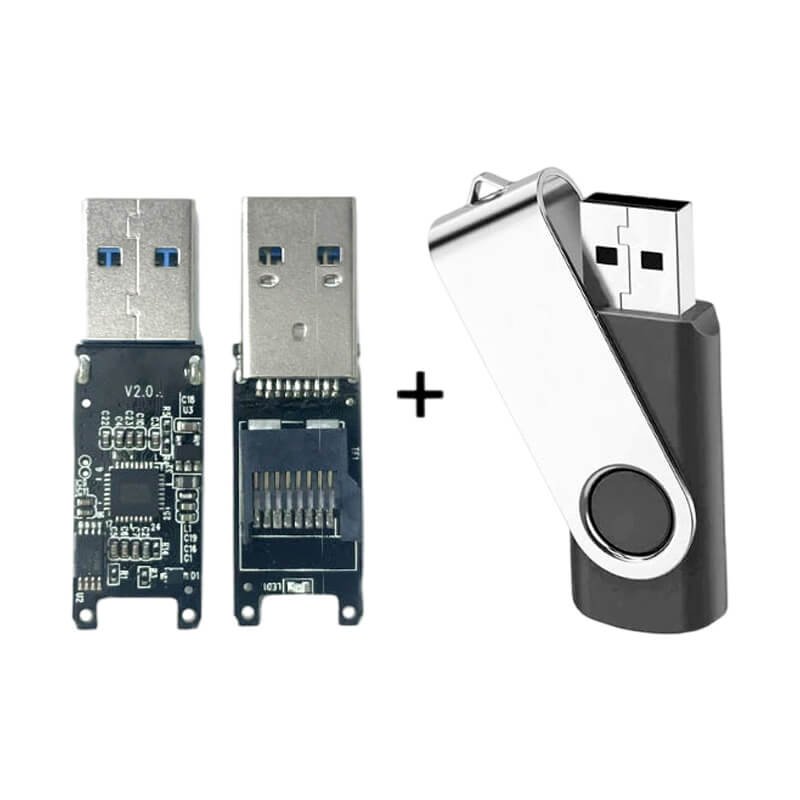
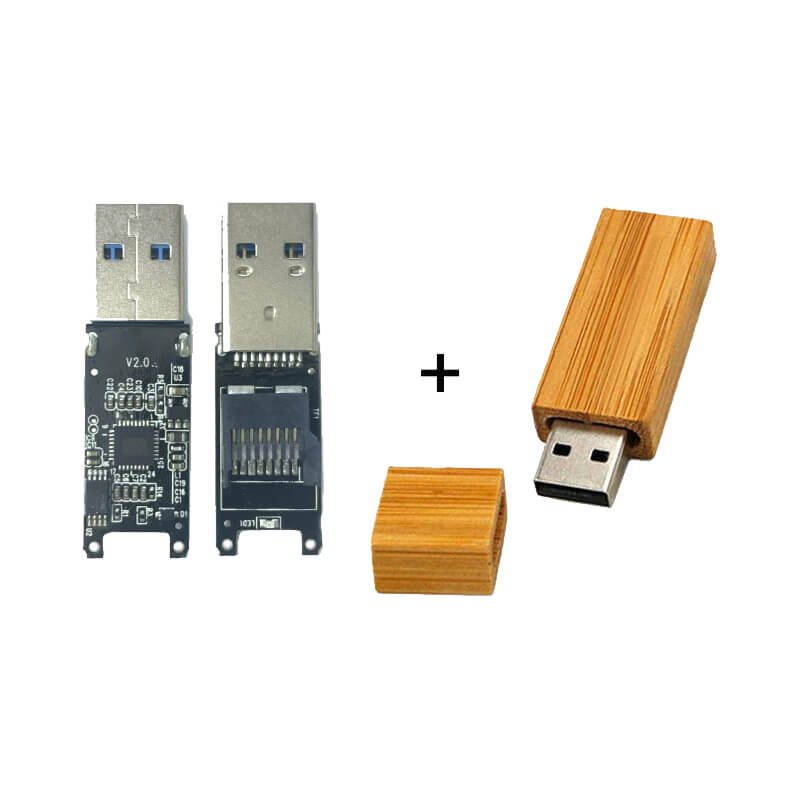



What is a USB flash drive composed of?
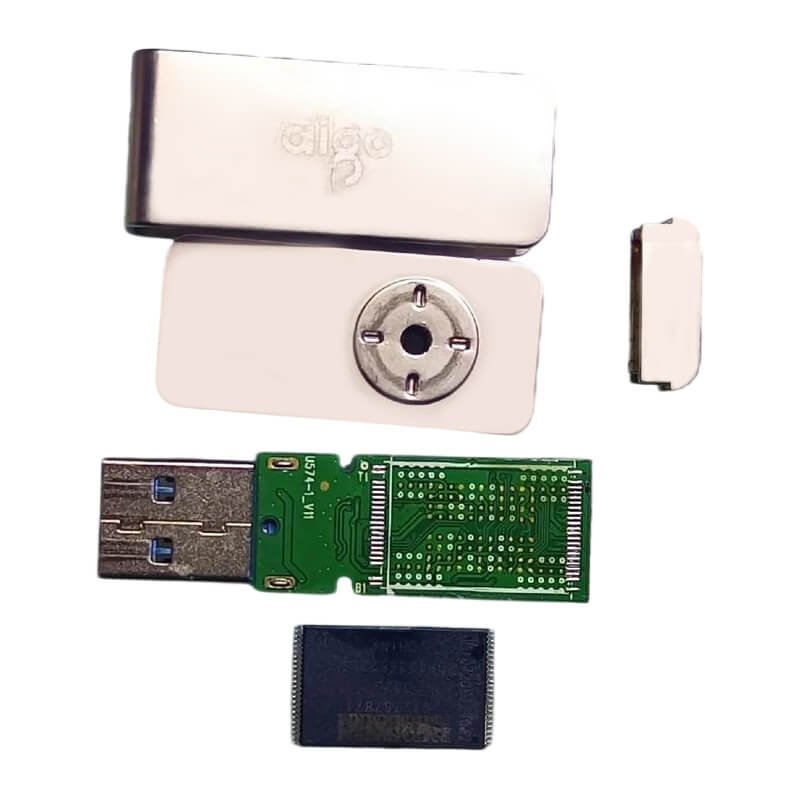
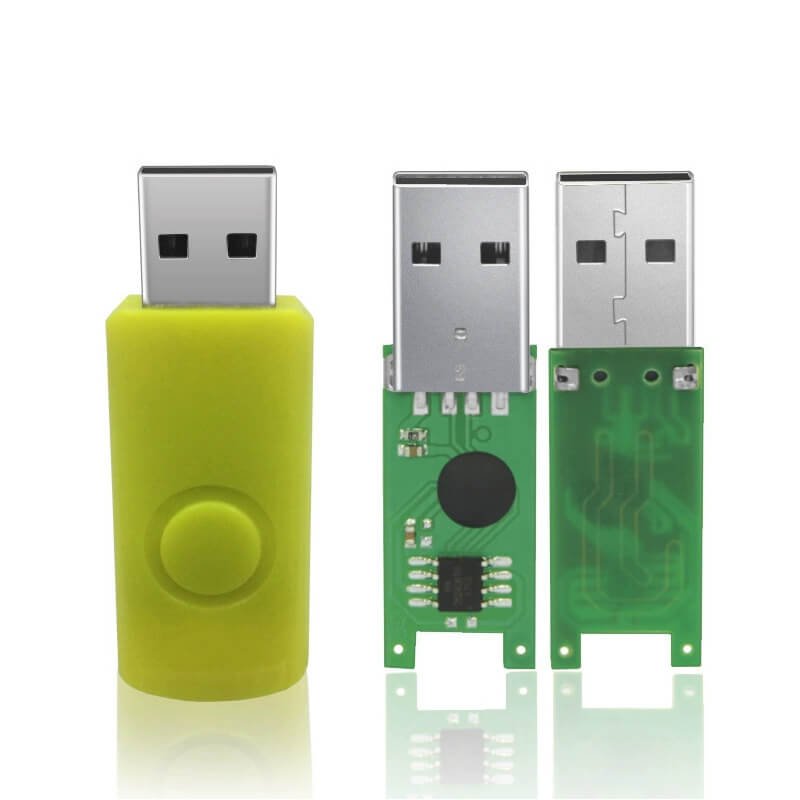
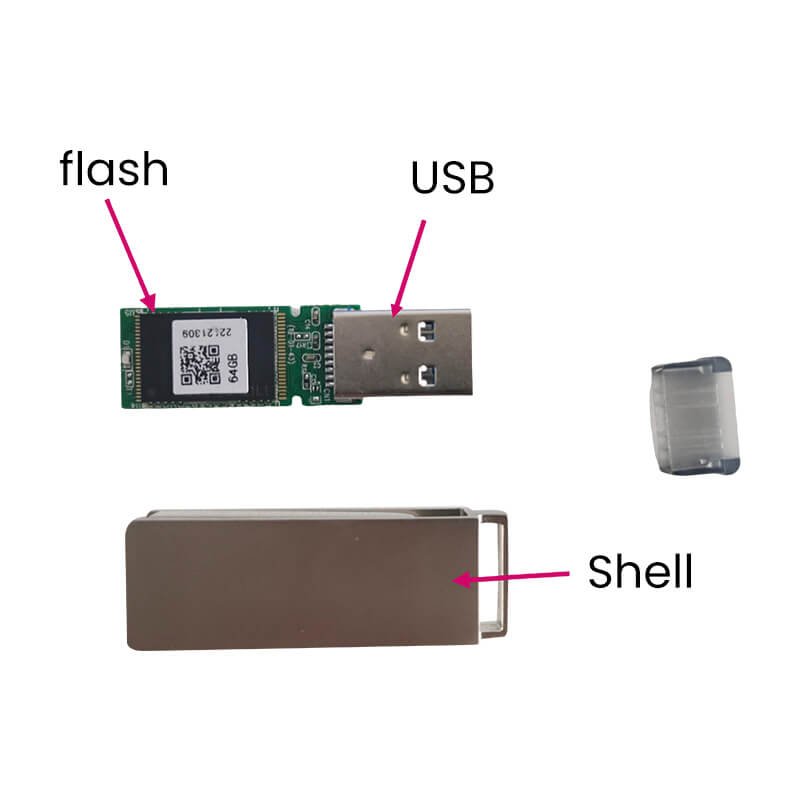
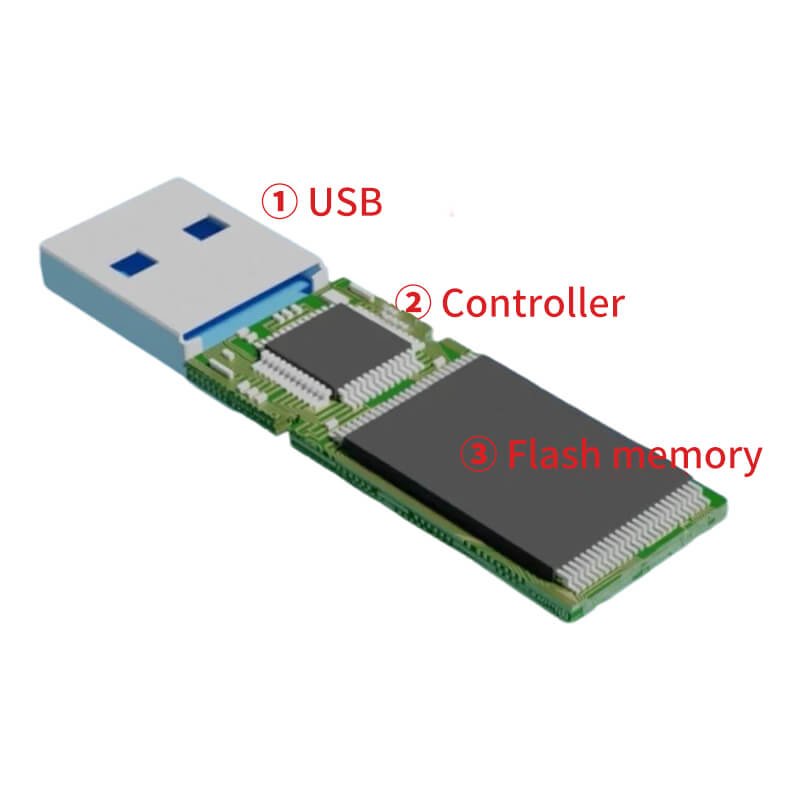
A USB flash drive mainly consists of three core hardware components: a flash memory chip, a controller chip, and a USB interface. The flash memory chip is responsible for storing data, the controller chip manages read and write operations and the file system, and the USB interface is used to connect to a computer or other devices. For mobile phone USB flash drive models, there are also TYPE-C interfaces or Android interfaces, which are used to connect to mobile phones. Simply put, the core of a USB flash drive is the storage chip plus the control chip, which realizes the plug-and-play data storage function through the USB interface.
Main Hardware:
The hardware structure of a USB flash drive determines its working method, which mainly consists of three parts:
- Flash Memory: This is the core component responsible for actually storing data. It is a non-volatile memory, meaning that data will not be lost after a power outage.
- Controller: It is equivalent to the “brain” of the USB flash drive. Its functions include managing data reading and writing, communicating with external devices (such as computers), and implementing wear leveling to extend the life of the flash memory.
- USB Interface: Its role is to physically connect the USB flash drive to external devices and realize the transmission of electrical signals.

Data Storage (Flash Memory)
The storage unit of a flash memory chip is a floating gate MOSFET. Its core is a “floating gate” that can capture electrons. The number of electrons on the floating gate is used to represent data (0 or 1):
- Writing Data: The control chip applies high voltage to make electrons break through the oxide layer insulation and inject into the floating gate (this process is called “programming”). When the floating gate captures electrons, the conductivity of the storage unit changes, representing “0”; when there are no electrons in the floating gate, it represents “1”. It should be noted that different types of flash memory, such as NAND flash memory, usually need to “erase” the original data first before writing, that is, to clear the electrons in the floating gate.
- Reading Data: The control chip applies low voltage to detect whether there are electrons in the floating gate. If there are electrons in the floating gate, the conductivity of the field-effect tube decreases, outputting “0”; if there are no electrons in the floating gate, the conductivity of the field-effect tube is high, outputting “1”. By detecting the differences in these electrical signals, binary data can be restored.
- Deleting Data: Flash memory cannot directly modify a single storage unit. When deleting, high voltage is needed to “extract” the electrons in the floating gate (called “erasing”), so that the storage unit returns to its initial state (usually “1”).


Data Interaction Principle (Controller)
After the USB flash drive is inserted into the USB interface of the computer, data interaction proceeds as follows:
- Identification and Communication: After the USB interface is powered on, the control chip wakes up and establishes communication with the computer’s USB controller. It exchanges device information such as capacity, model, and supported transmission modes through USB protocols (such as USB 2.0/3.0/3.1).
- Execution of Data Read and Write Commands: When the user operates files (such as copying, saving), the computer sends read and write commands and data addresses to the USB flash drive’s control chip. After parsing the commands, the control chip locates the corresponding storage block in the flash memory chip, performs write (programming + erasing) or read operations, and feeds back the processing results to the computer.
- Wear Leveling Technology: Since the number of erasing and writing times of flash memory is limited (for example, MLC flash memory is about 10,000 times, and TLC is about 3,000-5,000 times), the control chip will use a “wear leveling algorithm” to evenly distribute data to different storage blocks, avoiding overuse of a certain area, thereby extending the overall service life.


External Hardware
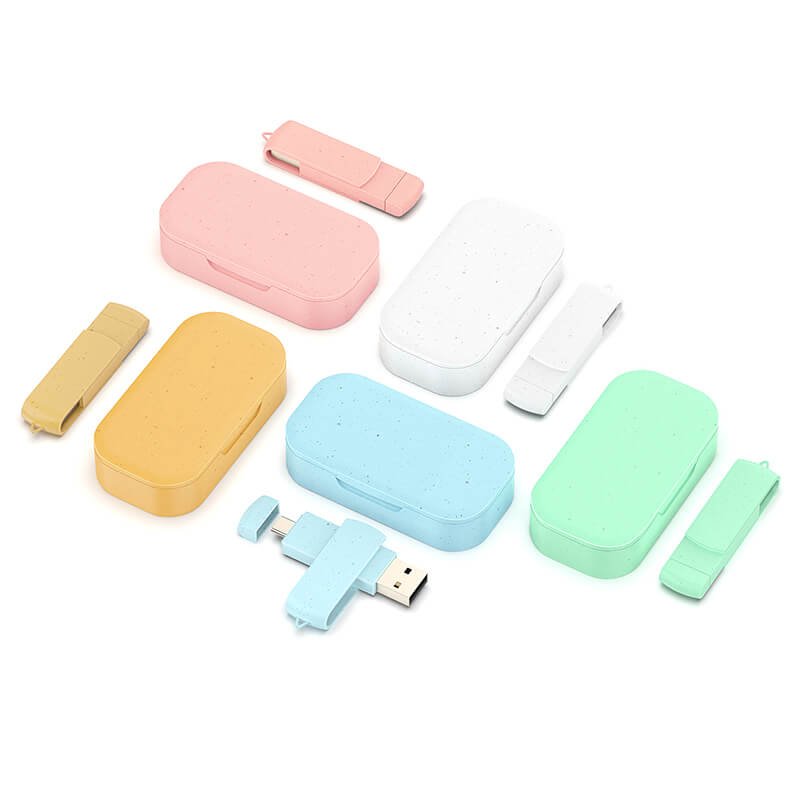
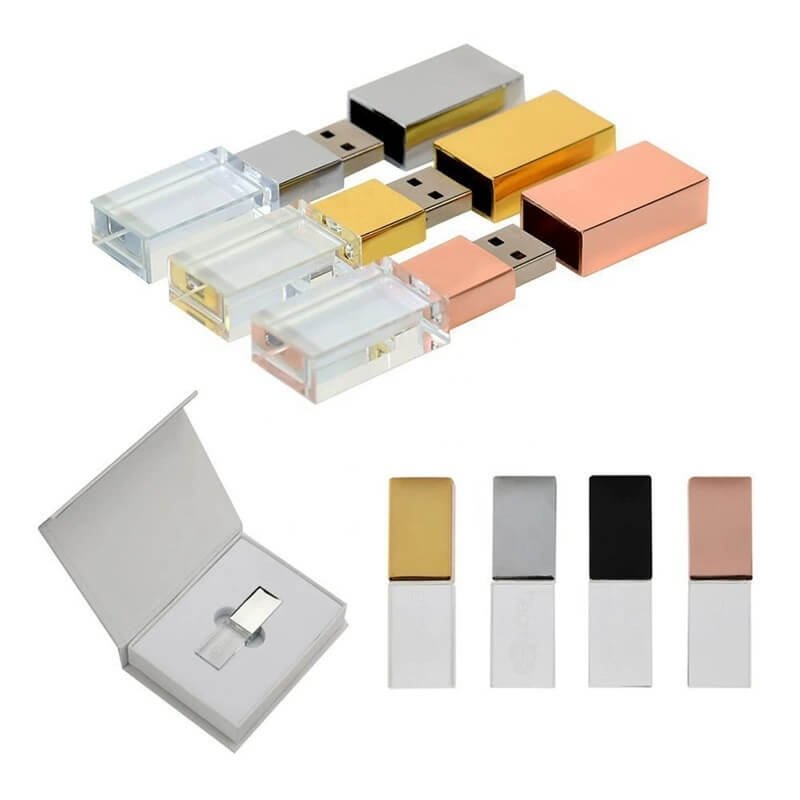
In addition to the three important components, a USB flash drive also includes a PCB circuit board and a casing. The circuit board is used to fix and connect the above three important components, and the USB flash drive casing provides protection and portability. The internal components of the USB flash drive are the same, but different casings show different appearances.
The PCB circuit board and the USB flash drive casing are essential external components of the USB flash drive. There are also optional components such as USB flash drive packaging, USB flash drive accessories like keychains, adapters, etc., which are the most common components of the USB flash drive.
What are the advantages of a USB flash drive?
- Storage Principle: Based on flash memory technology, it does not require a physical drive, relies on chips to store data, and data can be stored for a long time after a power outage.
- Portability: It is small in size (usually the size of a finger) and light in weight (mostly 10-30 grams), easy to carry around, and can even be hung on a keychain.
- Versatility: Adopting the USB interface standard, it has strong compatibility and can be connected to most computers, laptops, smart TVs, and mobile phones, tablets and other devices that support OTG functions.
- Ease of Use: It is a plug-and-play device. After being inserted into the USB interface, the device is usually automatically recognized, and no complicated drivers need to be installed (except for special systems). Users can directly copy, paste, delete files, etc.



What are the common uses of a USB flash drive?
- Temporarily storing and transferring files, such as documents, pictures, videos, installation programs, etc.
- Making a system startup disk for installing the operating system or repairing system faults.
- Serving as a carrier for mobile databases or applications, facilitating the use of specific software between different devices.
Differences between USB flash drives and other storage devices
Compared with traditional floppy disks and optical discs, USB flash drives have advantages such as large capacity (from tens of MB in the early days to several TB now), fast read and write speeds, shock and moisture resistance, and long service life (can be read and written tens of thousands of times or more under normal use). Therefore, they have gradually replaced floppy disks and optical discs and become one of the mainstream portable storage devices. However, in terms of large-capacity long-term storage, its cost performance is usually not as good as that of mobile hard drives.
Well-known USB flash drive brands
There are many other excellent USB flash drive brands on the market, such as PNY, HIKSEMI, Eaget, YOUSAN, etc. These brands have their own characteristics. When choosing a USB flash drive, users can comprehensively consider their own needs in terms of capacity, read and write speed, durability, price, etc., and also refer to the brand’s reputation and credibility to select the product that best meets their needs.
| Brand | Year Founded | Headquarters/Parent Group | Core Series and Interface | Maximum Read/Write Speed | Casing Material/Protection Performance | Warranty Period | Featured Functions and Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kingston | 1987 | USA | DataTraveler Elite G2(USB 3.1) | Read speed reaches high speed by series (specific value not specified) | Metal, waterproof, dustproof, shockproof | Lifetime warranty | Uses high-quality flash chips and main control chips for stable data transmission; over 2000 products covering all scenarios |
| SanDisk | 1988 | USA (a subsidiary of Western Digital) | Extreme Pro(USB 3.2) | Read: 420MB/s, Write: 380MB/s | Designed by series, focusing on durability | Extreme Pro/Extreme series: lifetime warranty; Ultra series: 5 years; 欣享 (Xinxiang)/ 欢欣 i 享 (Huanxin i Xiang) series: 2 years | All series come with data encryption software; cover high/mid/low-end needs by series; dual-interface design adapts to mobile phones and computers |
| Toshiba | 1875 | Japan | TransMemory(USB 3.0) | Fast read and write (specific value not specified) | Durable casing, suitable for frequent use | Not specified (usually 1-5 years by series) | Cost-effective, stable performance, suitable for daily office and storage needs |
| SAMSUNG | 1938 | South Korea | BAR Plus(USB 3.1) | Read: 300MB/s, Write: 150MB/s | Full metal body, waterproof, dustproof, shockproof, anti-magnetic | Not specified (usually long warranty for high-end series) | Adapts to complex environments, high-speed transmission with data security, beautiful appearance |
| HP | 1939 | USA | Multiple series (mostly USB 3.0 and above) | High-speed read and write (specific value not specified) | Innovative design, retractable structure | Not specified (usually 2-5 years) | Beautiful design, strong compatibility, suitable for office and study scenarios, with prominent convenience |
| aigo | Not specified | China | Multiple series | Excellent performance (specific value not specified) | Stylish appearance, some with dual interfaces (Type-A/Type-C) | Not specified (usually 1-3 years) | Cost-effective, dual-interface design adapts to multiple devices, meeting diverse office and study needs |
| Netac | 1999 | China | Consumer/industrial series | High-speed transmission by series | Professional storage design, focusing on stability | Not specified (usually longer for industrial series) | Pioneer in flash drives, with many core technology patents, products sold to over 60 countries, covering consumer and industrial scenarios |
| TECLAST | Not specified | China | Multiple series | Improving performance (specific value not specified) | Practical design, balancing durability and cost | Not specified (usually 1-3 years) | Outstanding cost performance, stable market share, providing economical storage options for consumers |
Through the above content, I believe you have a more comprehensive understanding of USB flash drives. Whether it is daily data transmission or system maintenance, USB flash drives can play an important role and are indispensable tools in digital life.




